In the US, the packaging is a leading business nowadays. Every business packaging plays a significant role in product brand awareness; it becomes a product identity and boosts sales. 3D printing is a critical technology in the packaging business. There are also many functions in product packaging that play a role in protecting the products during transportation. Packaging design plays a vital role in customer assistance and its uses.
Another functional role that packaging plays is that of assisting customers in identifying products. In packaging design, one should get enough details through text, images, and other forms of abstraction to quickly understand what product is inside the package. Colour can also be useful for denoting various models of a product within one brand. Packaging that includes brand items, like logos, brand colours and font variations, can also help customers identify the company that makes a product. It can also help new customers to get familiar with your brand and improve brand identity. Packaging is a brand awareness opportunity and should also become a source boosting sales of a product.
What is 3D Printing
Additive processes are used for the creation of 3D printed items or objects. 3D printing is the process of making a three-dimensional item from a digital file. In this process, an object/item is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced cross-section of the thing.
3D printing helps you out to produce complex shapes and designs using less material than traditional manufacturing methods.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
We will look at all 3D printing technologies and the processes involved with each of its applications.
STEREOLITHOGRAPHY (SLA)
It is known as the world’s first 3D printing technology. It was invented in 1986. It works by a 3D printing method called Vat Polymerization, where a material called a photopolymer resin (Transparent, Standard, High Temperature) in a tub is selectively vulcanized by a light source.
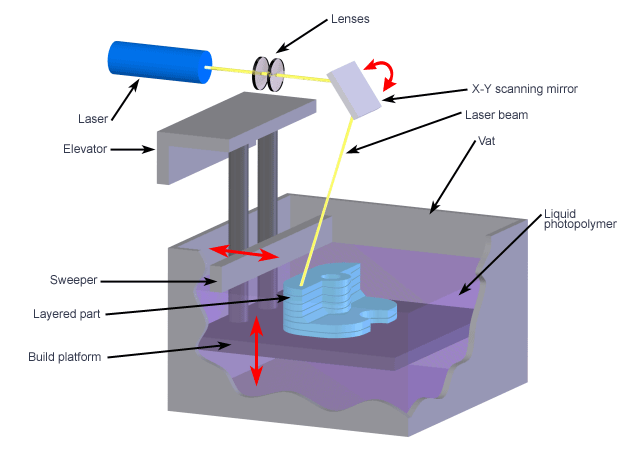
The SLA printer uses galvanometers, also called galvos, where one is positioned on the X-axis and the other on the Y-axis. These galvanometers aim at the point of a laser beam across the resin vessel, selectively curing and solidifying it by a cross-section of the object in the build area, building it up layer by layer for convenience.
SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING (SLS)
It is a 3D printing process called Powder Bed Fusion. A BIN of thermoplastic powder is heated to just below its melting point. Then, a wiper blade deposits a thin layer of the powder; it is usually 0.1 mm thick onto the build platform. A laser beam starts scanning the surface, where it selectively ‘sinters’ the powder, meaning it solidifies a cross-section of the item/object. As with SLA, the laser is focused on a location by a pair of galvanometers.

Once the whole cross-section is scanned, the platform moves down by one thickness of layer height, and the entire process takes another cycle until the object is fully ready to be done. Powder that is not sintered remains in place, supporting the thing that has been sintered, eradicating the need for support structures. Typical applications for SLS are manufacturing functional parts, complex ducting requiring hollow designs, and low-run production.
DIGITAL LIGHT PROCESSING (DLP)
A 3D printing technology and is almost the same type of machine as SLA. The core difference being DLP uses a digital light projector that flashes a single image of each layer all at one time. Light is projected onto the resin by light-emitting diode (LED) screens or an ultraviolet (UV) light source, such as a lamp. It is directed onto the build surface by a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD), an array of micro-mirrors that control where the light is projected and generate the light pattern on the build surface.
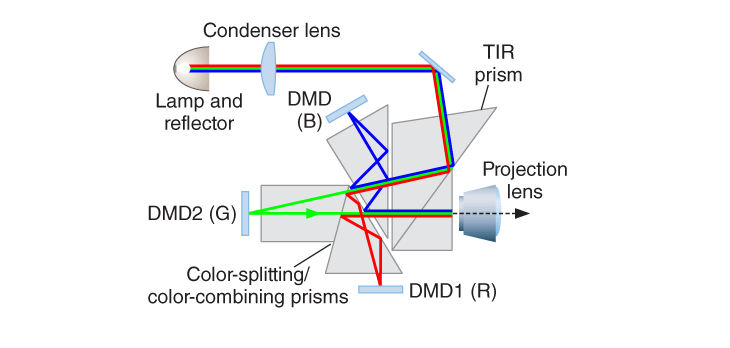
Since the projector is a digital screen, the image of each layer is made up of square pixels, so each layer is formed from small rectangular blocks called voxels.DLP has faster print times than SLA because each layer is exposed all at once instead of tracing the cross-section of an area with the point of a laser. Typical applications for SLA and DLP are injection mould-type polymer prototypes, jewellery, dental, watches, applications, and hearing aids.
FUSED DEPOSITION MODELING (FDM)
Sometimes called Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is a 3D printing technology that uses Material Extrusion. Material Extrusion devices are the most widely available and inexpensive of the types of 3D printing technology nowadays. They work by a process where a spool of the filament of solid thermoplastic material is loaded into the 3D printer. It is then pushed by a motor through a heated nozzle, where it melts. The printer’s extrusion head then moves along specific coordinates, depositing the 3D printing material on a build platform where the printer filament cools and solidifies, forming a solid object. Once the layer is complete, the printer lays down another layer, repeating the process until the thing is fully developed.
There are more technologies regarding 3D printing; the most used and essential technologies are discussed above.
Advantages of 3D Printing
Can Be Customized
One of the advantages of 3D printing is that it can easily customize like styles, designs and sizes. The main reason is that it is based upon computer-Aided-Design.
Cost-Effective
3D printing has a technological aspect, so people assume that it will be higher in pricing, but it is more cost-effective than traditional Printing.
Ideal for rapid prototyping
Because the technology allows for small setups, this process is ideal for prototyping, which means that products can be created faster than with traditional manufacturing techniques.
Affordable costs
No moulds are required; the costs associated with this manufacturing process are relatively low. The price of a part is directly related to the amount of material used, the time taken to build the part and any post-processing that may be required.
Conclusion
As we are living in a digital age, 3D Printing has more importance due to its advancement. Few highlighted technologies are discussed above for 3D printing; more technologies are material jetting, drop on demand, sand binder jetting, and metal-binding jetting. 3D printing left traditional printing far behind. It has many advantages, some are discussed above. 3D printing provides services in various industries Medicine, Automotive, Robotics, Packaging.


One thought on “A Guide for 3D Printing Technologies for Successful Packaging Business”